farmnatura
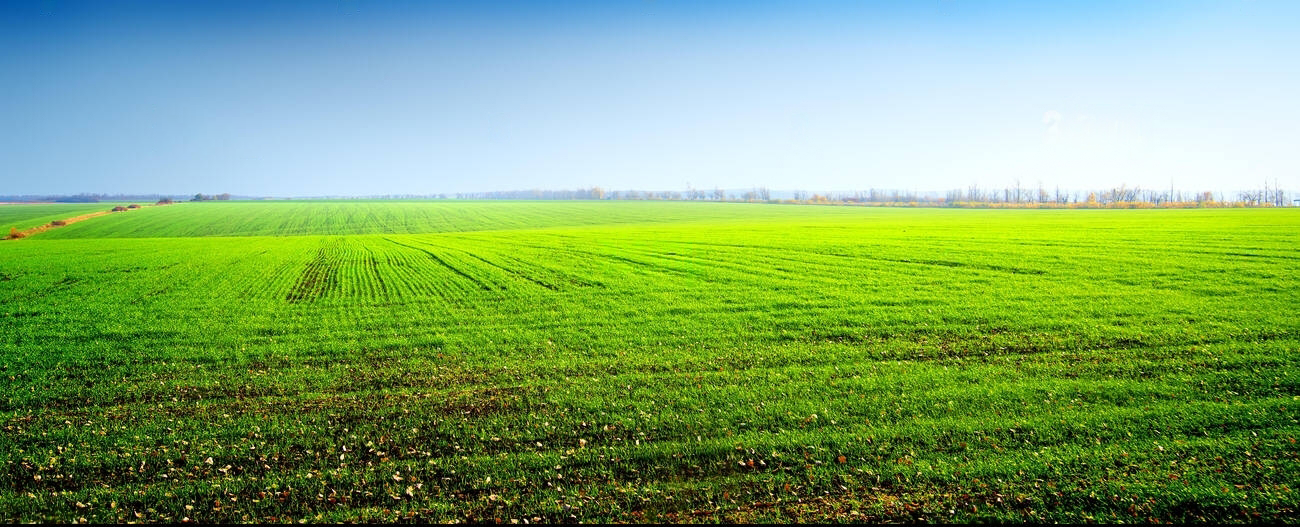
Determine Your Goals
Personal Use vs. Investment: Decide if you want the land for personal farming or as an investment for renting out or development. Type of Farming: Consider what type of farming you want to do (crop farming, livestock, organic, etc.) as this will affect the type of land you need. Location and Accessibility Proximity to Markets: Check how close the land is to markets, suppliers, and infrastructure like roads and utilities. Climate and Soil Quality: Assess if the climate and soil are suitable for your intended use. Different crops thrive in different conditions. Legal and Regulatory Considerations Zoning Laws: Understand local zoning laws and regulations that may affect what you can do with the land. Water Rights: Determine if the property has sufficient water rights for your needs, especially important for irrigation. F
Financial Feasibility Purchase Price: Compare prices of similar properties in the area to ensure you're paying a fair price. Operating Costs: Estimate ongoing costs like taxes, maintenance, and utilities. Environmental Factors Conservation and Sustainability: Consider environmental factors and how they align with your values and practices.
Infrastructure and Facilities
Existing Structures: Evaluate existing buildings or infrastructure (barns, irrigation systems) that may add value. Future Development: Plan for any additional facilities or improvements you might need in the future. Consult Professionals Real Estate Agent: Work with a real estate agent specializing in agricultural properties to navigate the buying process. Legal and Financial Advisors: Seek advice from professionals familiar with agricultural investments to ensure all legal and financial aspects are covered. Due Diligence Property Inspection: Conduct a thorough inspection of the land and its features to identify any potential issues. Title Search: Verify the property’s ownership history and any existing liens or easements. Long-Term Planning Financial Planning: Consider long-term financial planning and potential returns on investment. Risk Management: Plan for contingencies such as crop failures, economic fluctuations, or regulatory changes. Negotiation and Purchase Make an Offer: Once satisfied with your research, negotiate the purchase terms and conditions.

farmnatura
Buying Farm Land

Buying farmland can offer numerous advantages, both financial and personal. Here are some key benefits to consider.Appreciation in Value: Farmland historically appreciates in value over time, driven by factors like population growth, urban sprawl, and increasing global demand for food. Stable Asset: Farmland is often considered a stable investment compared to other types of real estate, as food production is a fundamental need. Income Generation Rental Income: If you're not farming the land yourself, you can lease it to farmers for income, providing a steady cash flow. Crop Revenue: If you farm the land, you can generate revenue from selling crops or livestock. Tax Advantages Tax Deductions: Farmland ownership can offer tax deductions for expenses such as maintenance, property taxes, and depreciation of equipment. Capital Gains Tax Treatment: Farmland may qualify for favorable capital gains tax treatment if held for a certain period. Diversification. Portfolio Diversification: Farmland can diversify your investment portfolio, reducing overall risk by adding an asset class that typically behaves differently from stocks and bonds. Hedge Against Inflation: Agricultural land tends to maintain its value during inflationary periods, providing a hedge against rising prices. Long-Term Value Generational Wealth: Farmland can be passed down through generations, preserving wealth and providing a tangible legacy for your family.
Control Over Land Use: Owning farmland gives you control over how the land is used and managed, allowing you to implement sustainable practices or conservation efforts. Environmental Benefits Conservation Opportunities: Farmland ownership provides opportunities to implement conservation practices, such as wetland preservation, wildlife habitat creation, or sustainable agriculture techniques. Carbon Sequestration: Well-managed farmland can contribute to carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change. Lifestyle Considerations Personal Fulfillment: Many people find owning and working on farmland to be personally fulfilling, offering a connection to nature and a slower-paced lifestyle. Health Benefits: Growing your own food can provide fresh, healthy produce and promote physical activity. Community and Social Impact Support Local Economy: By investing in farmland, you support local farmers and contribute to the vitality of rural communities. Educational Opportunities: Farmland ownership can provide educational opportunities for learning about agriculture and sustainable land management practices.
